Image via Wikipedia
Image via Wikipedia
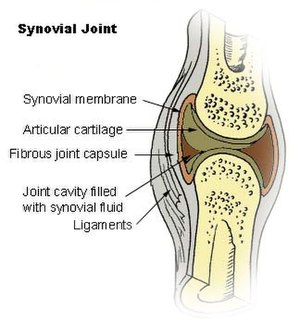
Gout is a medical condition that is characterized by recurrent bouts of sudden stiffness, burning pain, and swelling of a joint, most commonly the big toe. The attacks of gout can recur and over time, the condition can harm the joints, tendons, and other tissues if not treated early.
Although it most often affects the large joint of the big toe, gout can affect other joints including the knees, ankles, feet, elbows, wrists, and hands. It frequently affects one joint at a time. But in chronic cases, it can affect several joints.
Gout is caused by excessive uric acid in the blood, but not all people with elevated uric acid levels develop gout. Gout can seem to flare up without any specific cause.
Some factors are known to bring about gout attacks such as obesity. A high purine diet or a diet that is rich in meat and seafood is another contributing factor. Other factors that may elevate uric acid in the body are certain medicines, rapid weight loss, chronic kidney disease, high blood pressure, and hypothyroidism.
It has been noted that men who drink alcohol may double their likelihood of developing gout. Researchers believe that although genes and environmental factors may lead to gout, regular alcohol consumption has caused an increase in cases of gout in the past three decades. Compared to other alcoholic beverages, beer contains much higher amounts of purines.
The researchers believe that alcohol consumption increases the risk of gout. Alcohol has high purine content that leads to an increased purine load. The digestive process then breaks down the purine compounds, leading to the formation of uric acid. When the uric acid is deposited in the joints, it leads to gout formation by stimulating an intense inflammatory reaction. The result is painful, red, and swollen joints.
Alcohol may also contribute to obesity, which in turn is associated with inadequate excretion of uric acid.
To prevent gout, avoid fish, particularly anchovies, crab, mackerel, sardines, and shrimps. Other foods to avoid are meat, organ meats, and meat extracts. People with history of gout should avoid excessive alcohol consumption or refrain from drinking alcohol altogether.
A gout supplement with cherry extract can help alleviate gout symptoms and has helped many gout sufferers.
Although it most often affects the large joint of the big toe, gout can affect other joints including the knees, ankles, feet, elbows, wrists, and hands. It frequently affects one joint at a time. But in chronic cases, it can affect several joints.
Gout is caused by excessive uric acid in the blood, but not all people with elevated uric acid levels develop gout. Gout can seem to flare up without any specific cause.
Some factors are known to bring about gout attacks such as obesity. A high purine diet or a diet that is rich in meat and seafood is another contributing factor. Other factors that may elevate uric acid in the body are certain medicines, rapid weight loss, chronic kidney disease, high blood pressure, and hypothyroidism.
It has been noted that men who drink alcohol may double their likelihood of developing gout. Researchers believe that although genes and environmental factors may lead to gout, regular alcohol consumption has caused an increase in cases of gout in the past three decades. Compared to other alcoholic beverages, beer contains much higher amounts of purines.
The researchers believe that alcohol consumption increases the risk of gout. Alcohol has high purine content that leads to an increased purine load. The digestive process then breaks down the purine compounds, leading to the formation of uric acid. When the uric acid is deposited in the joints, it leads to gout formation by stimulating an intense inflammatory reaction. The result is painful, red, and swollen joints.
Alcohol may also contribute to obesity, which in turn is associated with inadequate excretion of uric acid.
To prevent gout, avoid fish, particularly anchovies, crab, mackerel, sardines, and shrimps. Other foods to avoid are meat, organ meats, and meat extracts. People with history of gout should avoid excessive alcohol consumption or refrain from drinking alcohol altogether.
A gout supplement with cherry extract can help alleviate gout symptoms and has helped many gout sufferers.